Shipping goods from China to Canada has become increasingly common due to the growth of e-commerce and global trade. As businesses expand their reach into international markets, understanding the shipping process is essential for ensuring timely delivery while managing costs and compliance with regulations. This comprehensive guide will cover everything from shipping methods, customs requirements, packaging considerations, to insurance options.
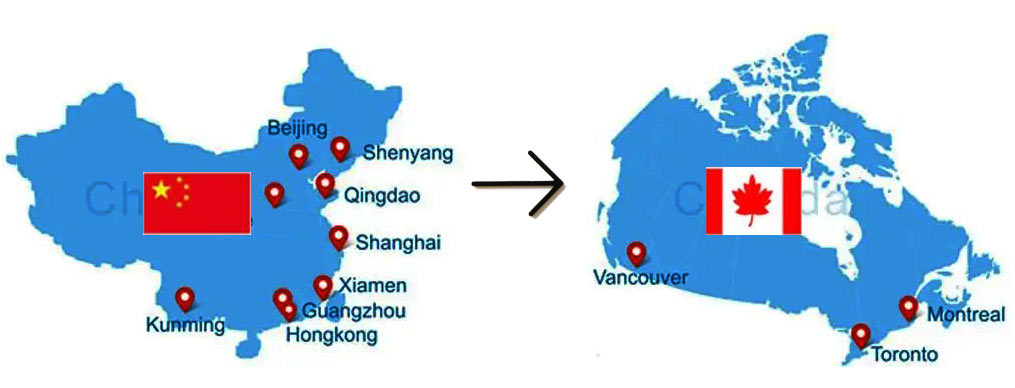
The shipping process from China to Canada involves several key steps:
Selecting the right shipping method is crucial for balancing speed, cost, and efficiency. The primary options include air freight, ocean freight, rail freight, and express shipping. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, which we'll explore in detail.
Proper documentation is vital for smooth customs clearance and delivery. Essential documents include commercial invoices, packing lists, bills of lading, and certificates of origin. Ensuring these documents are accurate and complete can help avoid delays.
Packaging plays a significant role in protecting products during transit. Using appropriate materials and clearly labeling packages are key factors that can contribute to successful shipping.
Navigating Canadian customs regulations is critical when shipping goods internationally. Understanding the necessary paperwork and duties involved will help prevent unexpected costs or delays.
Cargo insurance should be considered to protect against potential loss or damage during shipment. Evaluating the risks associated with the goods being shipped can inform decisions about coverage.

Air freight is the fastest shipping method available, typically taking between 1-5 days for delivery. Businesses often choose air freight for urgent shipments.
Advantages:
Speed: Quick delivery times make it ideal for time-sensitive items.
Global Reach: Available for most international locations and facilitates access to remote areas in Canada.
Tracking: Most air freight services provide detailed tracking options, allowing shippers to monitor their shipments in real-time.
Disadvantages:
Cost: Air freight is significantly more expensive than other shipping options, which can be prohibitive for small businesses or low-cost items.
Weight and Size Restrictions: There are limits on the weight and dimensions of packages, making it less suitable for bulk shipments.
Environmental Impact: Air freight has a higher carbon footprint compared to sea freight.
Ocean freight is used for transporting large volumes of goods and is typically more economical than air freight.
Advantages:
Cost-Effective: Suitable for bulk shipments with lower freight costs per unit.
Capacity: Ships can accommodate a vast range of cargo, including oversized items.
Environmental Sustainability: Generally, ocean freight is more environmentally friendly compared to air freight.
Disadvantages:
Transit Time: Shipping by sea can take weeks (2-6 weeks on average), which may not suit businesses with tight deadlines.
Port Limitations: Goods must be transferred to trucks or trains for final delivery after reaching a port, adding additional time.
Customs Delays: Longer customs clearance times may occur due to the volume of goods processed at ports.
Express shipping is a premium service offered by courier companies for quick deliveries.
Advantages:
Fast Delivery: Packages can arrive within 1-3 business days.
Convenience: Door-to-door delivery simplifies the shipping process for businesses.
Comprehensive Tracking: Allows continuous updates on shipment status.
Disadvantages:
High Cost: Express shipping is significantly more expensive than standard options.
Size and Weight Limits: There are restrictions on the size and weight of parcels.
Complex Customs Processing: Although many express services manage customs, regulations must still be followed carefully.

To help businesses decide which shipping method is best for their needs, here’s a comparative analysis of air freight, ocean freight, rail freight, and express shipping:
| Shipping Method | Speed | Cost | Best For | Limitations |
| Air Freight | 8-15 days | High | Urgent shipments | Weight/size restrictions |
| Ocean Freight | 4-6 weeks | Low per unit | Bulk goods | Slow transit times |
| Express Shipping | 3-6 days | Very high | Time-sensitive packages | Size and weight limits |
Proper documentation is essential for trouble-free customs clearance and shipment processing. Here are the key documents often required when shipping from China to Canada:
This document details the sale transaction between the buyer and seller. It should include:
The packing list provides specific details about the contents of each package or container. It should include:
A bill of lading serves as a contract between the shipper and carrier, detailing the transportation of goods. It includes:
This document certifies that goods were manufactured in a particular country. It's often required for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements.
Certain goods may require import permits depending on their nature. Researching these requirements ahead of time can prevent delays.
Depending on the type of goods being shipped, additional documentation such as health certificates, phytosanitary certificates, or technical standards compliance may be needed.
Understanding Canadian customs regulations is vital when shipping internationally. Here’s a breakdown of the key components involved in customs clearance:
Goods imported into Canada may be subject to various duties and taxes, including:
Goods and Services Tax (GST)
Provincial Sales Tax (PST) or Harmonized Sales Tax (HST)
Calculating these costs beforehand can help businesses plan their budgets more accurately.
Tariffs are taxes imposed on specific goods entering Canada. The amount depends on the classification of the product under the Harmonized System (HS) code. Consulting with a customs broker can ensure correct classification and compliance with tariffs.
Canada has free trade agreements with multiple countries, including the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) with the European Union and the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA). Businesses should investigate whether their products qualify for tariff exemptions under these agreements.
Hiring a customs broker can simplify the customs process. Brokers are experts in customs regulations and can help businesses navigate the paperwork and compliance requirements efficiently.
Effective packaging is crucial for protecting goods during transit, meeting shipping regulations, and ensuring efficient handling. Here are some best practices for packaging items when shipping from China to Canada:
Choosing durable packaging materials such as corrugated boxes, bubble wrap, or foam inserts can provide adequate protection against damage during transportation.
Proper labeling with clear identification of the contents, destination address, and any necessary handling instructions (e.g., "Fragile" or "Keep Dry") can minimize mishaps during transit.
Reducing excess packaging helps cut shipping costs as carriers charge based on dimensional weight. Ensuring that boxes are appropriately sized for their contents can lead to significant savings.
Different shipping methods have specific packaging requirements. For example, air freight requires adhering to weight and size regulations while ocean freight may necessitate moisture-resistant packaging.
While many shipments arrive safely at their destination, it's prudent to consider insurance coverage to protect against potential loss or damage. Here are some insurance options to keep in mind:
Cargo insurance covers goods while in transit. It's generally offered by freight carriers or specialized insurance companies. Policies can vary, so reviewing the coverage details and exclusions carefully is essential.
Some carriers offer declared value coverage, which allows shippers to declare the value of their goods for compensation purposes in case of loss or damage. However, this option may come with limitations.
Third-party insurance providers can also offer coverage tailored to specific needs. Comparing quotes and policy features can help businesses find the best option that fits their requirements.
Effective tracking of shipments is crucial for maintaining transparency and ensuring timely delivery. Here are some best practices and tools for tracking shipments from China to Canada:
Most freight carriers provide online tracking systems that allow shippers and recipients to monitor the status of their shipments in real-time. By entering a tracking number, you can view details such as:
For businesses that frequently import goods, utilizing inventory management software can streamline tracking processes. These systems can integrate with carrier APIs to automatically update shipment statuses and inventory levels.
Maintaining open communication with your suppliers in China is essential. Regular updates on shipping schedules, potential delays, or changes can help you manage expectations and plan accordingly.
Many carriers and logistics platforms offer alert features that notify you via email or SMS about significant milestones in the shipping process, such as when the shipment is out for delivery or if there are any customs issues.
Shipping can sometimes encounter unexpected challenges. Here’s how to effectively handle delays and other issues:
If a shipment is delayed, the first step is to identify the cause. Common reasons include:
Stay in contact with your freight forwarder or shipping company to get updates on the situation. If necessary, communicate with your customers about potential delays to manage their expectations.
After resolving the current delay, analyze what went wrong and how to prevent it in future shipments. This may involve improving documentation processes, better communication with suppliers, or adjusting shipping methods based on past performance.
Familiarize yourself with your contract terms with the carrier regarding delays. Understanding your rights can help you in negotiating solutions or seeking compensation if applicable.

To ensure smooth and efficient shipping processes, consider the following tips:
Establishing solid partnerships with reliable suppliers in China can facilitate smoother shipping experiences. Good communication leads to better understanding and fewer misunderstandings regarding timelines, product specifications, and packaging requirements.
Select a freight forwarder or logistics provider with experience in international shipping. Check reviews, ask for referrals, and inquire about their specific expertise with shipments from China to Canada.
Customs regulations can change frequently. Regularly review the latest updates on Canadian import laws, tariffs, and trade agreements to remain compliant.
Consider consolidating smaller orders into larger shipments to reduce overall shipping costs. Bulk shipments often have lower per-unit shipping expenses compared to multiple small shipments.
Review your shipping methods periodically to determine if they still meet your business needs. Changes in your product line, order volumes, or customer demands may necessitate adjustments in shipping strategies.
If possible, experiment with various shipping carriers to compare service quality, delivery times, pricing, and customer support. This knowledge can lead to improved decision-making in the long run.

Navigating the complexities of sourcing Chinese goods for distribution in Canada requires strategic planning and optimal communication. A thorough understanding of regulatory policies and logistics is also vital. Adherence to international best practices and access to appropriate resources can significantly enhance shipping operations, minimize costs, and ensure timely delivery.
Regardless of your different levels of experience in international shipping, these insights can help develop a robust global trade shipping strategy to meet both your business and customer satisfaction goals.
With persistent dedication and adaptability, success can be achieved in the exciting realm of international trade.